
Gel: An Amazing Substance
Advanced Science
746 views
0 likes
You will need to sign in before you can comment or like.
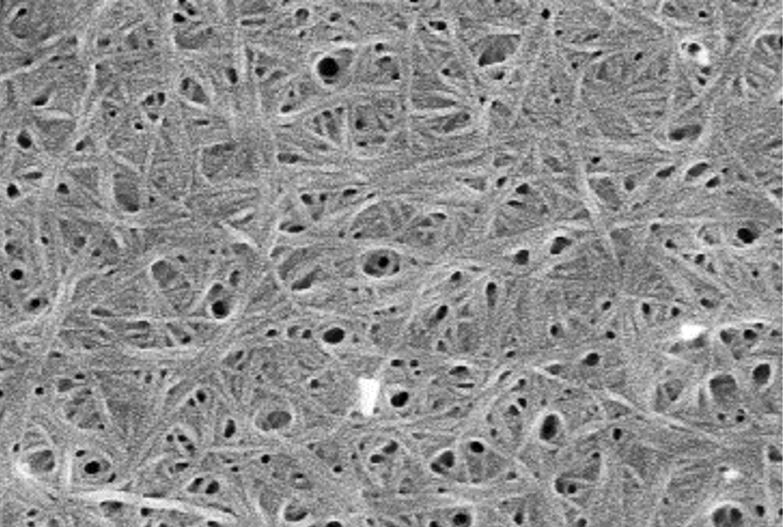
Amongst different class of soft materials, gels are very much fascinating not only
because of their unique properties but also for their crucial application in our
daily life. Essentially, gels are semi-solid viscous materials capable of immobilizing
large amount of solvent molecules upto 1000 times of their dry weight inside the
crosslinked hierarchical three dimensional network structure. Once the solvent
molecules get trapped, flow behavior is lost unless the network structure is
disrupted by heating or some other external factors. Now, if the trapped solvent
is water, then gel is called hydrogel and if, organic solvents, then gel is called
organogel. After removing the solvent from gel network, the gel is called
Xerogel.
Gels are classically made from high molecular weight natural polymers,
synthetic polymer molecules along with naturally occurring biopolymers such as
polysaccharides, proteins, DNA or synthetic small organic molecules. What we
use as toothpaste is basically a polymer gel. Similarly, ketchup is also a gel.
When shaken, it starts flowing, and on release of stress it gets re-solidified to form
gel again. This behavior of the gel is called Thixotropy. Other daily life gels we
use are jam, jelly, hair gel, cosmetics, ointments and as additives in different
food products. Hydrogels also exist naturally in the body system
as mucus, vitreous humor of the eye, cartilage, tendons and blood clots. Their
viscoelastic nature results in the soft tissue component of the body, disparate
from the mineral-based hard tissue of the skeletal system.
In recent years, researchers have designed and developed gels with the
introduction of bio-functionality, biodegradability and biocompatibility along
with stimuli responsivity. Heat, pH, pressure, light, additives are stimulus to name
a few. This development is for the fulfillment of practical purposes such as drug
delivery (as delivery vehicle), tissue engineering (tissue growth and repair), bioimaging,
therapeutic application along as template for nano-fabrication.
Now a days, the gels are designed to be used in separating oil, toxic metal,
dyes etc. from water bodies. In conclusion, gels are promising soft materials
having unique properties and outstanding versatility.
Comments